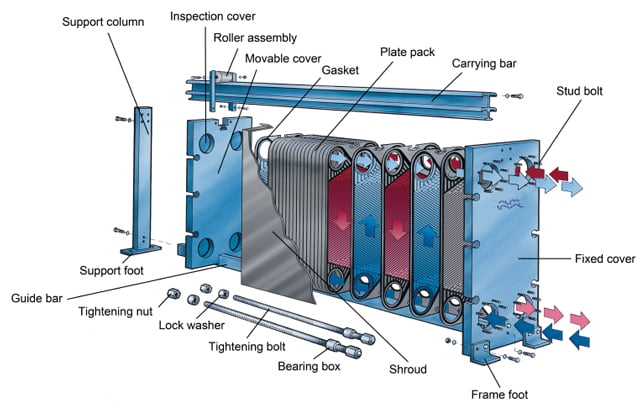
There's a common misconception in the industry that all gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers are the same, no matter the brand. However, there are quite a few design features that can have a significant impact on your operation. The plate-and-frame features highlighted below are important components to look for in a heat exchanger, and when combined, these features offer extensive benefits, including:
 CurveFlow™ Distribution Area
CurveFlow™ Distribution AreaOne of the most important features of a plate heat exchanger, the CurveFlow distribution area optimizes the flow of media for better utilization of the whole plate surface and reduces the risk of fouling.
An inefficient distribution area with uneven flow causes maldistrubution and fouling build up.
 ClipGrip™ gaskets
ClipGrip™ gasketsClipGrip gaskets are glue-free and offer superior alignment that ensures a perfect seal and trouble-free maintenance. Fastening to the plate is improved by having five fastening points.
Other gasket designs, such as snap-in gaskets, only have one fastening point to the plate. If this one point is lost, there is no gasket fastening function.
 Five-point alignment
Five-point alignmentThe five-point alignment system ensures perfect plate alignment when closing the unit, and makes removing plates during maintenance quick and easy.
Many alignment systems do not close the vertical gap between the carrying bar and the plate, leading to wavy plate packs with leaking problems.
The offset, zig-zag gasket groove offers the greatest possible heat transfer area by better utilizing the plate surface area.
Other gasket groove designs can result in the need for more plates and reduced thermal efficiency.
The OmegaPort noncircular inlet and outlet saves energy by enhancing the flow of media to give increased throughput, lowering pressure drop, and optimizing utilization of the plate surface.
Circular ports are less efficient and can result in increased energy and pump costs.
The performance of a heat exchanger is influenced by different components and places very high demands on the gasket system. To obtain highest performance, it is important that the plate and gasket are designed together.
Many gasket suppliers apply a “one size fits all” low cost production philosophy, which can cause premature leakage, gasket damages or misaligned plate packs.
Corner guiding keeps plates aligned throughout the entire plate package during closing of the heat exchanger. The plates are designed with corners that lead the plates into position and help stabilize the plate pack during the tightening procedure.
The lack of a proper alignment system may allow the plate pack to move in any direction, leading to wavy plate packs with leakage problems.
In order to achieve the best sealing in semi-welded models, the weld is positioned separately - outside the ring gasket, ensuring equal sealing force over the entire port hole gasket and guaranteeing high performance through the welded channel.
The sealing weld is commonly placed inside the ring gasket groove. This combined with an uneven port hole groove creates a risk of the weld joint forming a rough surface against the sealing gasket, leading to gasket stress and failure.
Should either of the two gaskets in contact with the fluids fail: the leaking fluid will enter the leak chamber and then be drained to the atmosphere via the venting ports. The leakage will thus be detected early, which means less production losses.
Without the leak chamber or venting ports, failure of a gasket with subsequent leakage of a fluid could have severe results.
A metal part attached to plates in the hanger section prevents damage to plates.
A pressed collar is the most common type of reinforcement used in the market today. This is a good reinforcement on smaller plates, but not for heavy ones and can lead to damage, especially when frequent cleaning is necessary.
Glue between the gasket and the metal plate safeguards high quality bonding for the toughest operating and service conditions. A two-component oven-cured epoxy glue, that can only be removed from the plates by special treatment, will keep the gasket on the plate during cleaning.
Gaskets attached to a plate with rubber glue, oven-cured or not, does not achieve a strong enough bond, which can result in gaskets falling off during cleaning, when the temperature gets critical or when aggressive fluids make the gaskets swell.
 Bearing boxes
Bearing boxesPlate-and-frame heat exchangers that have tightening bolts with bearing boxes reduces friction when opening and retightening the unit, making it possible for one person to service the heat exchanger without special tools.
Plate heat exchangers with standard washers involve time consuming adjustments to all tightening bolts. The lack of bearing boxes also increases the force applied and the risk of paint damages to the frame plate, which leads to corrosion damage and ultimately the need to change frame plate.
 T-bar roller design
T-bar roller designThe T-bar pressure plate roller is mounted under the carrying bar, decreasing the height of the heat exchanger and making maintenance simpler and more cost-effective.
The mechanical solution of the roller can be more or less robust. The risk is a pressure plate that is jammed and impossible to move when it is time to conduct service.
Swing feet can simply be swung to the side for service, allowing for quick and easy opening of the unit while maintaining its seismic rating.
Most plate heat exchangers have feet that are bolted or welded to the frame and/or pressure plate. These feet are more likely to get stuck, and they also have to be completely removed for servicing.
The fixed bolt head makes assembly fast and safe since it prevents the nut from loosening during opening and closing of the heat exchanger. The bolt head is fixed through mechanical deformation of the threaded bar with the bolt head in place, preventing it from rotating.
Sometimes bolt head are fixed using glue, which can deteriorate under tougher operating conditions, such as high temperature and/or an aggressive environment. Consequently, service will take more time and if the bolt head shoots away from the tightening bolt, injuries or damage may occur.
A cover for tightening bolts prevents them from corrosion. Look for both grease and a plastic cover as protection.
Tightening bolts without a cover are prone to corrode after some time in operation, even though the bolt is covered in grease at delivery.
Key hole bolt openings make it much easier to attach the bolts along the side of the heat exchanger and make for fast and safe assembly. The necessary installed foot print and service area is also much less, since the tightening bolts can be removed sideways.
Service can be time consuming on designs with drilled holes, since the nut on the tightening bolt has to be completely removed. The required area of the plate heat exchanger must be larger, since the tightening bolts must be pulled out through the drilled holes.
Elongated nuts located on the tightening bolt on the pressure plate side prevent overheating and tightening bolt failure.
A standard nut size runs the risk of overheating and seizing. The consequences are added service time and, in the worst case, the need for a new nut and tightening bolt.
Lock washers are used for the tightening bolt, making the assembly job much faster as the lock washer prevents the nut or bolt head from rotating during opening and closing.
Without a lock washer, the nut on the pressure plate has to be held stationary while another spanner loosens the tightening bolt from the frame plate side so the nut on the pressure plate doesn't spin with the bolt.